Exploring Farmworkers and Food Justice in Vermont
“There is this violent irony in our food system, in that the people who provide food security for all of us are the most likely to be food insecure themselves”. This was the heart of the message shared by University of Vermont Scholar Teresa Mares at a recent gathering at the Middlebury Unitarian Universalist Society. Mares was sharing insights gleaned during research for her book Life on the Other Border: Farmworkers and Food Justice in Vermont, which aimed to shed light on the intersections of structural vulnerability and food insecurity experienced by migrant farmworkers in the northeastern borderlands of the United States.
By the Numbers
Half of all workers on U.S. dairy farms are migrants and most are from Mexico. Losing them would double the total retail price of milk and cost our nation’s economy more than $32 billion. Across the U.S., Latinx farmworker food security occurs at 3-4 times the national average and Mares recognized that there was a lack of data on food security among farmworkers in Vermont. Through her research, Mares was able to identify that there are approximately 1,000-1,200 Latinx migrant workers sustaining the Dairy Industry in Vermont. Most of these individuals are from Southern Mexico, but some also come from Central America. These workers are mostly men, but steady numbers of migrant women are also employed on Vermont’s dairy farms. They are concentrated most heavily in Franklin and Addison County.
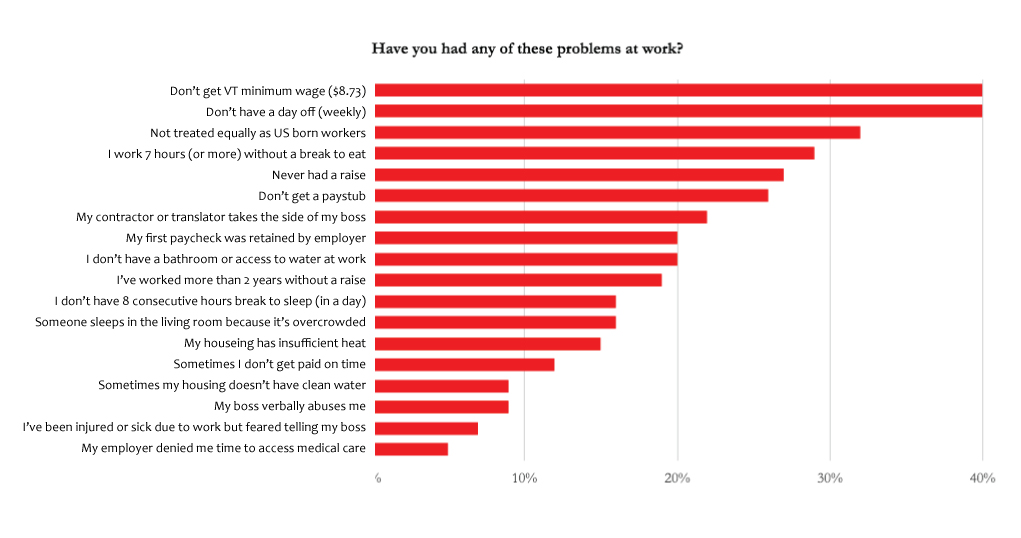
Roughly 90% of these workers are undocumented, due in large part to the fact that dairy workers are ineligible to work seasonally on farms on an H2A Visa, as is common in Vermont’s apple industry. A whopping 68% of Vermont’s milk comes from dairies employing migrant laborers, representing annual sales of $320 million, translating to 43% of New England’s milk supply. These individuals pay taxes, yet they’re unlikely to have the opportunity to utilize any of the resources that their tax dollars support. They are not eligible for food assistance resources like 3-Squares VT or WIC unless they have a U.S. born child and even then, they must be able to endure the risk of exposure associated with the completion of a government form.
After surveying 100 migrant farmworkers (75 men and 25 women) in Vermont, Mares discovered that 18% of the state’s migrant farmworkers experience food insecurity, meaning they lack reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food. She also recognized that these numbers fail to paint a completely accurate picture of the data, as the standard USDA survey that is used to asses food security operates on the assumption that if one has money then one must have access healthy food. This assumption fails to account for the various other barriers that the average migrant farmworker experiences when trying to access healthy food. The reality for most migrant farmworkers is that access presents a greater challenge than financial instability. The survey also makes assumptions about what constitutes a household. Migrant farmworkers are often living in cramped quarters with many of their peers and are thus not representative of a typical household. Given this multitude of factors supported by information gathered during a series of in-depth interviews with farmworkers, Mares determined that 50% or more of farmworker households likely struggle with access to food.
Challenges to Access
When working 70 or more hours per week without a day off, as is the reality for most migrant dairy workers, it can be rather difficult to find time to shop for groceries. Add to that the rural isolation, lack of transportation, and a crippling fear of deportation experienced by a migrant farmworker living in a predominantly white community located well within the 100-mile jurisdiction of U.S. Customs and Border Protection, and it’s easy to understand why most members of this community (96%) rely on a third-party to access food. Mares also shared that there’s limited access to culturally-appropriate food in Vermont and a general lack of awareness of the kinds of food available in many stores. If you’ve never been able to enter a Vermont grocery store, you can only take your best guess as to what might be available when preparing your grocery list for a third-party shopper. Additionally, when you’re living in a household with 5 or more adults and you’re only able to shop every 15 days, there becomes a need for a significant amount of refrigerated storage space that is often lacking in the substandard housing where these individuals live. Mares expressed her strong belief that any strategies aimed at alleviating food insecurity among this group must be willing to travel to the farms and meet the farmworkers where they are.
Resiliency
While it’s clear that Vermont’s Dairy Industry is heavily reliant on migrant farmworkers from a financial perspective, Mares challenged those in attendance to avoid measuring the worth of this hard-working group of individuals in economic terms. Their true value to our community runs much deeper. Mares’ book sheds light on the many ways that these individuals display resiliency and creativity in the face of a very challenging and isolated existence. They’re a culturally-rich group of people who often possess agricultural knowledge that far exceeds the actual farmwork that they’re employed to do and our failure to engage with them as members of our community results in a lost opportunity for valuable and meaningful cultural exchange.
Thanks to their brave willingness to organize and advocate for better working conditions, combined with the efforts of organizations such as the Huertas Project, the Addison Allies Network, Migrant Justice, and the Open Door Clinic, creative solutions are emerging to help support and foster increased resiliency among our migrant farmworker communities. We’re grateful to Teresa Mares for her willingness to shed light on this important issue and we’re grateful to the local organizations that are finding solutions to the challenges Mares outlined in her work. We look forward to exploring ways to support this effort.